A Smart City IoT Data API that registers sensors and ingests time-stamped readings.
- Stores the core info needed for each sensor.
- Fields:
sensor_id(PK): Unique id for each sensortype: Type of sensor (e.g. air_quality, temperature)latandlng: Geographic coordinates of the sensordescription: description of the sensorcreated_at: Timestamp when the sensor was registered. We usetoTimestamp(now())to get the current timestamp while storing.
-
Fields:
sensor_id: Id to link the reading to a sensor (kind of FK in RDBMS)timestamp(Clustering Key): When the reading was taken. Helps order the data (we use it for querying)value: The numeric reading (e.g. air quality value).unit: The unit of measurement (e.g PPM)status: The status of the reading (e.g. ok, warning).
-
Notes --
- Time-Series Data: Using
sensor_idas partition key andtimestampas clustering key supports efficient time-range queries. - High Write Throughput: Designed to handle a large number of writes from sensors.
- TTL Support: Can use Cassandra’s TTL to automatically remove old data. [TODO]
- Time-Series Data: Using
- Apache Cassandra (v5.x)
- Node.js & Express with DataStax Cassandra Driver
Compared to Traditional Databases (MySQL/Postgres) and MongoDB
-
High Write Throughput: Cassandra is designed to handle many writes per second (with very low latency), which is ideal for time-series sensor data. Can easily load balance across multiple nodes in a Cluster...
-
Scalability: It scales horizontally very easily; new nodes can be added without downtime (Mongo can also do this)
-
Distributed Architecture: There is no single point of failure. Data is automatically replicated across multiple nodes (No master/slave setup)
-
Tunable Consistency You can balance between consistency and performance by choosing the right consistency level
-
Time-Series Support: With its partition and clustering keys, Cassandra naturally supports time-series data models..
-
Built-In TTL Easily set expiration times on data, automatically cleaning up old sensor readings (caches like Valkey(Redis), Memcached do this often)
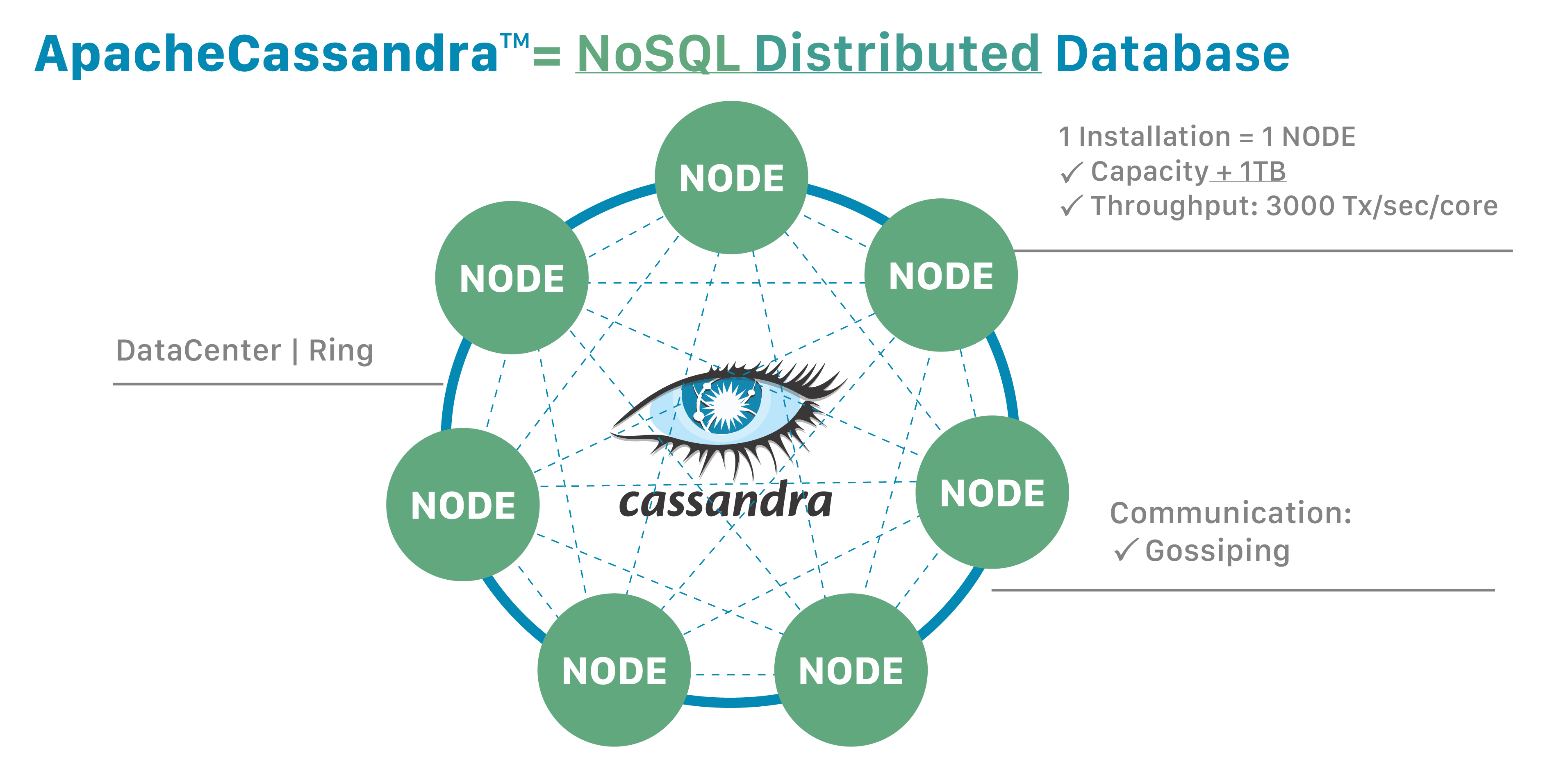
- P2P Architecture:
- Every node in the Cassandra cluster is equal. There is no master node.
- Partitioning:
- Data is divided across nodes using partition keys, ensuring balanced load
- Replication:
- Data is replicated across multiple nodes. The replication factor is configurable
- Consistency Levels:
- Cassandra lets user choose the consistency level for each operation, balancing performance and data accuracy.
- Write Path:
- Writes are fast because data is first written to a commit log, and then stored in an in-memory table (SST, memtable) before being flushed to disk.
- Read Path:
- Uses SSTables (Sorted String Table or SST) and bloom filters to quickly locate data on disk.
- Compaction:
- Compaction is a process that merges SSTables to reduce disk usage and improve performance. It is automatically triggered when the number of SSTables exceeds a certain threshold (as a batch process)
- Tombstone:
- A tombstone is a special marker in Cassandra that indicates that a row has been deleted. It is used to optimize read performance by skipping deleted rows.
This repo is released under the MIT License and can be used for any purpose.